Top 2 Benefits of Customer Retention
Customer retention is a key issues on every e-commerce business. Let's talk about why customer retention is so advantageous and best approaches for customer retention!
Sep 21, 2023
Contents
1. Why customer retention is so advantageous?1-1. Customer retention is up to 25 times less expensive than acquiring a new one.1-2. Retained customers can be the best evangelists.2. Best 3 Approaches For Customer Retention2-1. Segmentation2-2. Customer journey optimization2-3. Personalization3. The most important 3 indicators for customer retention3-1. Retention Rate3-2. Cohort Chart3-3. Churn Rate1. Why customer retention is so advantageous?
In today's dynamic business landscape, customers have countless options when choosing a brand or service that best fits their needs. This abundance of choice compels brands and service providers to continuously jostle for market share and requires more effort to acquire new customers. As a result, many businesses have begun to focus on strategies that encourage their existing customers to continue buying within their ecosystem. This approach is known as customer retention.
Customer retention refers to the strategies and efforts that a business employs to keep its existing customers engaged, satisfied, and loyal over an extended period of time. It is the process of maintaining and nurturing the ongoing relationship between a company and its customers after the initial sale or interaction. You may heard customer retention is a critical aspect of business success. But why is retaining customers so advantageous, and is it truly beneficial? If so, how can this be achieved? This article delves into the importance of customer retention and introduces the most advanced strategies to achieve it.
1-1. Customer retention is up to 25 times less expensive than acquiring a new one.
Harvard Business Review, a leading magazine and a wholly-owned subsidiary of Harvard University, states that acquiring a new customer is anywhere from 5 to 25 times more expensive than retaining an existing one. For instance, if you'd like to buy a new shampoo for anti-thinning hair, you'd first need to search for it. Various criteria might influence your decision, such as price, popularity, reviews, and ingredients, making the selection process time-consuming. Simultaneously, brands compete for your attention, escalating marketing costs. However, once you've bought a product and found it satisfactory, you're likely to repurchase it. If you've already established trust with the brand when buying other products like body wash in the past, their shampoo would likely be top-of-mind for you.
As the example explains, when you try to acquire a new customer, the funnel the lead has to pass through is quite extensive. Your brand should be visible to the customer during their search, and any considerations they have should be addressed on platforms where they frequent, such as blogs, SNS, or reviews. These activities are costly. However, re-engaging your existing customers is relatively simpler. You can bypass the initial stages of the funnel and directly encourage them to return using CRM or a retargeting campaign. In the most favorable situations, furthermore, you might not even need to do anything at all.
1-2. Retained customers can be the best evangelists.
If your customers return to your business, it means they are genuinely satisfied with your brand. Satisfied customers are the best brand ambassadors, as they are more likely to recommend your products or services to friends, family, and colleagues, regardless of what aspect of your business has satisfied them. Their satisfaction isn't necessarily limited to product quality; it can also relate to factors such as price, customer service, or design. These elements represent your brand's core values, and satisfied customers play a crucial role in spreading them. This phenomenon is known as word-of-mouth marketing, which contributes to the organic growth of your brand.
Word-of-mouth (WOM) marketing is key to a brand's organic growth, alongside customer retention. In general, if an existing customer brings in 0.2 to 0.3 new customers, that's a positive outcome. A score of 0.2 means that one out of every five existing customers has brought in a new customer, and if they bring in two new customers, it becomes 0.4, which is truly remarkable. Although this paper primarily focuses on customer retention and doesn't delve deeply into WOM marketing, it's important to recognize the amplification effect (where five existing customers bring in one new customer, that new customer subsequently brings in 0.2 new customers later, and this happens infinitely). This underscores the critical role of WOM marketing, which should rely on satisfied customers.
Returning to the original topic, your retained customers bring in new customers and the customers will bring in another one if they are also retained. So, how can you enhance customer retention?
2. Best 3 Approaches For Customer Retention
Customer retention is very important for e-commerce brands at any stage. In the early stages, building a fandom becomes essential especially when you have a limited advertising budget. In the middle or later stages, you may experience a slower growth of new customer acquisition, making customer retention the most effective way to increase revenue. Let's discuss the simplest steps to enhance customer retention.
2-1. Segmentation
If you treat all your customers as one, you may make many errors. It's essential to identify the various characteristics of customers to gain a deeper understanding of them. Segmenting customers based on their activity on your website, such as adding products to the cart, viewing certain products, or reaching the checkout page, can be beneficial. These are key factors in optimizing your website's funnel. However, no matter how satisfied your customers are with your website, they won't return if they're disappointed with your products. Thus, in order to enhance customer retention, it's important to analyze your customers with the ordering patterns.
There are two primary ways to segment your customers based on the transactional patterns.
- rule-based segmentation
- RFM-based AI segmentation
Segmentation implies treating your customers in different ways. A prime example of rule-based segmentation may be simply dividing customers into two groups: loyal customers and the rest. Of course, you need criteria to define who the loyal customers are. One of our customer companies makes loyal customers who constantly order the product at least once a month. However, this approach still remains the dilemma; how would you define a more loyal customer: one who made a single purchase of $2,000 or one who made ten purchases of $100 each?
Many AI-powered SaaS providers use the RFM model, which evaluates the recency, frequency, and monetary value of customers. "Recency" refers to how recently they made a purchase, "Frequency" indicates how often they purchase, and "Monetary" measures the total amount they have spent. The RFM model addresses the dilemma above by automatically segmenting these customers into distinct groups. Furthermore, the model could identify other groups that exhibit latent characteristics.
2-2. Customer journey optimization
The item journey reveals which products customers purchase in your brand. It helps answer questions like, 'What products do customers who have bought product A typically purchase next?' and 'Which products attract loyal customers, and what do they buy subsequently?' This is why analyzing the item journey is essential.
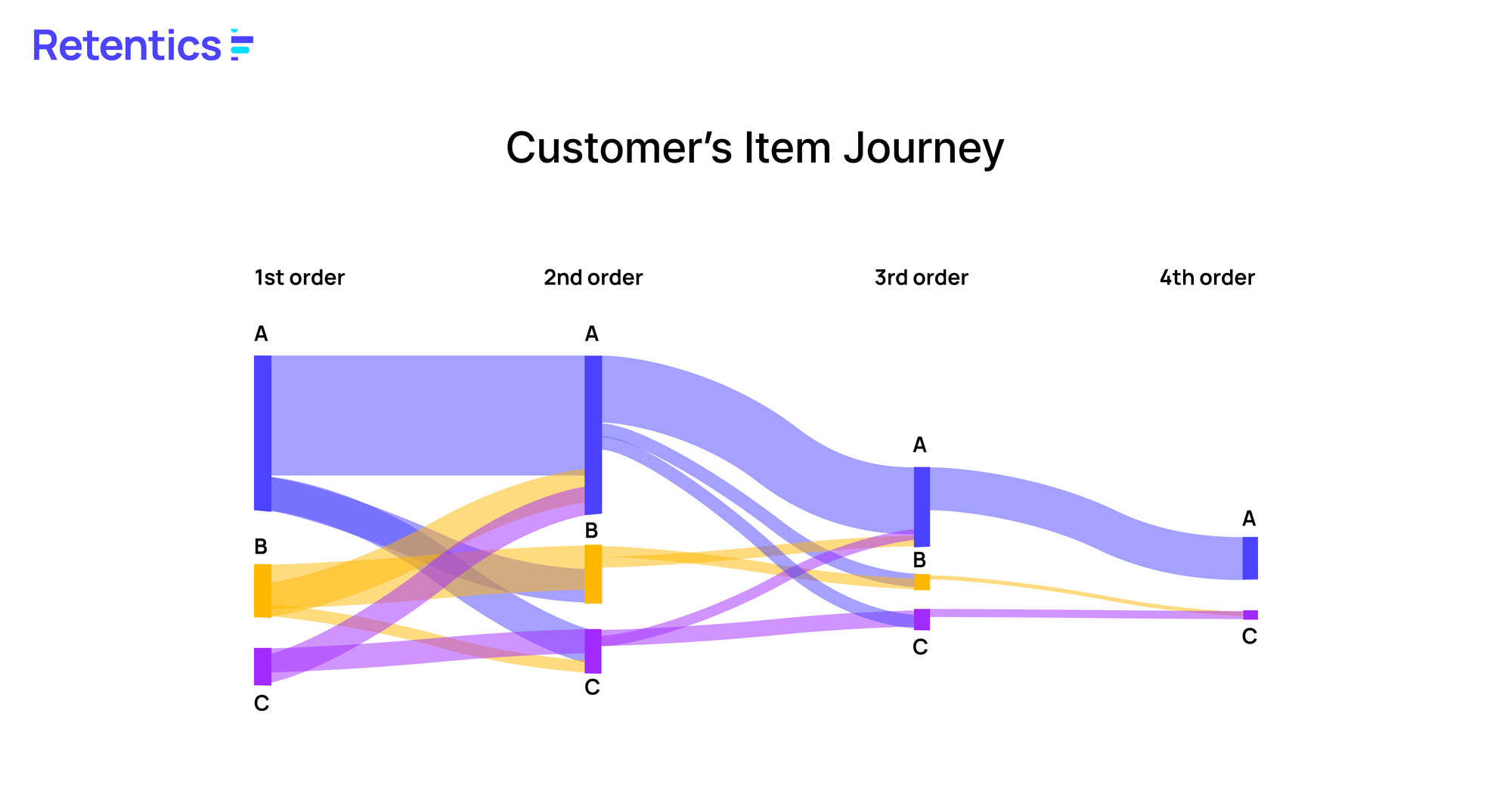
Even customers who make the same number of purchases (e.g., three purchases) may have different sequences of product purchases. For instance, one customer may purchase products in the sequence A - A - B, while another customer may follow the sequence C - B - A. Additionally, customers who purchase products in the same sequence may have different purchase intervals. For example, one customer might purchase A - A - B with 20-day intervals, while another customer might purchase it with intervals of 10 days, 20 days, and 20 days.
The item journey is a method used to understand customers' purchasing patterns. By examining item journeys across different segments, you can suggest the next most popular product for that particular group. For instance, if a customer buys product A and then product B a few weeks later, you can identify the most popular subsequent product in that sequence and recommend it to the customer. Additionally, by comparing the buying patterns of loyal customers with those of regular customers, you can guide regular customers towards the purchasing habits of the loyal ones. For example, if loyal customers tend to purchase in the sequence A - B - C, while regular customers buy in the order D - C - A, you can encourage the regular customers to adopt the more prevalent purchasing sequence of the loyal customers.
One important point to note is that customer segmentation is necessary before understanding item journeys since doing so based on the entire customer can be misleading due to the averaging effect.
2-3. Personalization
Hyper-personalization has become a common term for e-commerce businesses as AI technology thrives. When your customers visit your landing page, you can display different content to guide them toward the intended action. Additionally, on the checkout page, you could recommend additional products for cross-selling or upselling marketing promotions. Lastly, you can send CRM messages to your customers with a more personalized structure, specifying when, what content, and to whom. In this section, we are focusing on the last aspect, personalized CRM, as it is the easiest one to execute instantly.
There are various methods for personalized CRM messages. The most basic method is recommending the same product for the next purchase cycle. Additionally, rule-based messages are used to send reminders to customers who have taken specific actions in the app or online store. For example, the Uber Eats app in the United States sends a coupon push notification to customers who added food to their cart but did not check out after about fifteen minutes. This method reportedly leads to very high conversion rates. However, applying the same rule to all customers will lead to diminishing efficiency over time. Therefore, increasingly advanced personalized target messages are required.
Here are some examples of product recommendation algorithms but only based on the transactional data:
- Deep Learning Model: An advanced machine learning model for predicting the next purchased product.
- Association Analysis: Identifying patterns where customers who purchased product A later purchase product B.
- Customer Purchase Journey: Statistical information about the next journey based on the purchase history of each customer.
- Demand Forecasting Model: Predicting the next purchase time for each customer and the demand for specific products in the near future.
.png%3Ftable%3Dblock%26id%3D756ecd41-96d3-49f3-9676-16ae6694c6c3%26cache%3Dv2&w=3840&q=75)
However, these models are likely to perform poorly compared to simply recommending popular products if you don’t take into account the specific characteristics of e-commerce. The Retentics Analytics team has also optimized these models by collaborating with over dozens of clients. If your team doesn't have abundant resources, blindly hiring a team to build models is likely to result in unpredictable cost overruns.
3. The most important 3 indicators for customer retention
3-1. Retention Rate
retention rate is the most intuitive number to measure the retention rate. The formula is very simple. If you want to get the monthly retention rate;
Retention Rate = This Month And Last Month Active Customers / Last Month Active Customers
For instance, if 100 customers bought products last month, and out of those customers, 30 bought products again this month, the retention rate for this month is 30%. Calculating the retention rate requires some analytics because you need to identify the number of customers who made purchases in both this month and last month.
However, if your products do not require repeat purchases within a month, the calculation is getting more complicated since you may need to calculate the retention rate on a quarterly or annual basis. For example, if your brand sells a large size of body wash, and your customers mostly buy it every 3 months, you need to calculate the monthly retention rate for the quarterly retention. This means you need to identify the customers who have made a purchase both this month and at any time over the last three months, which sounds a bit more complicated than the monthly retention rate for the monthly retention.
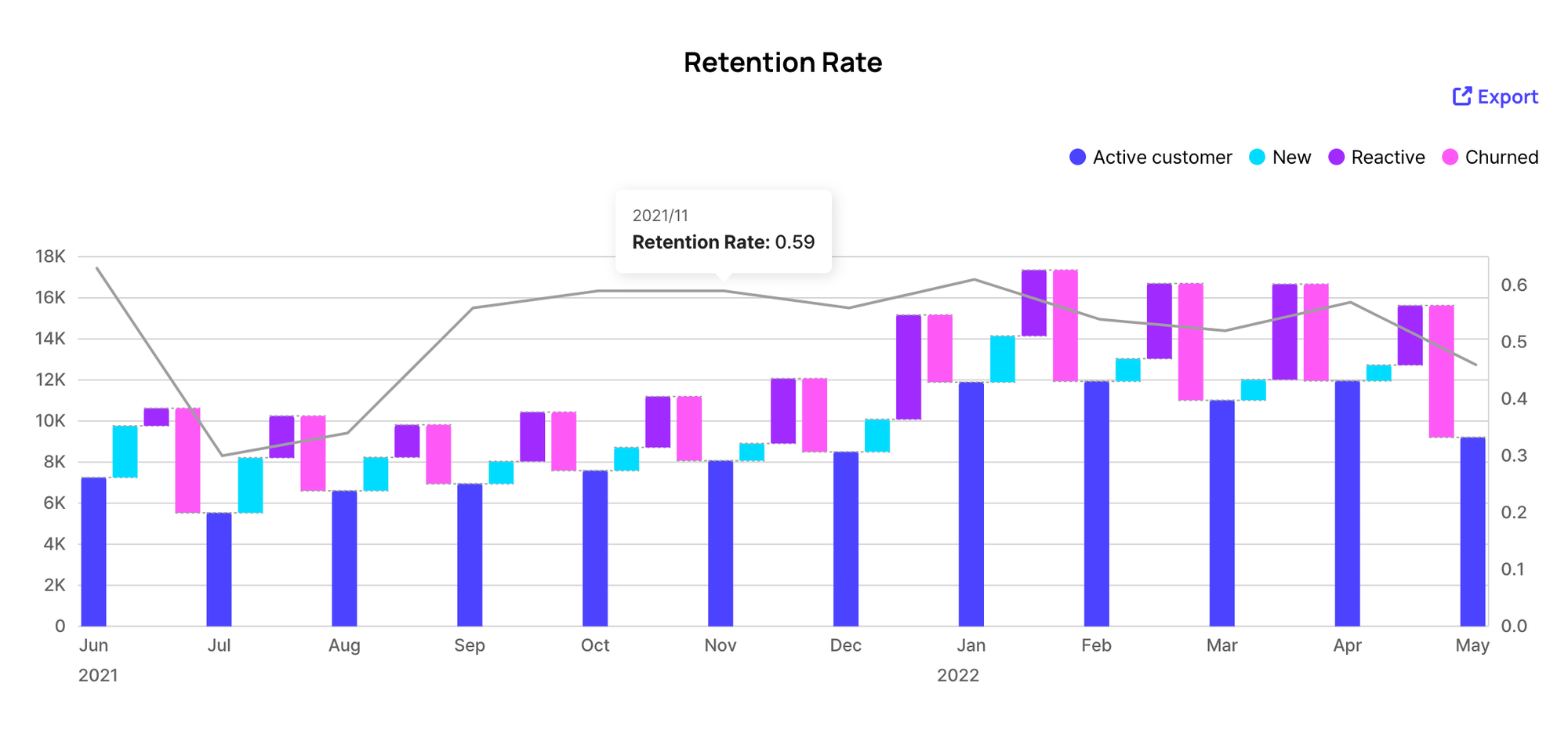
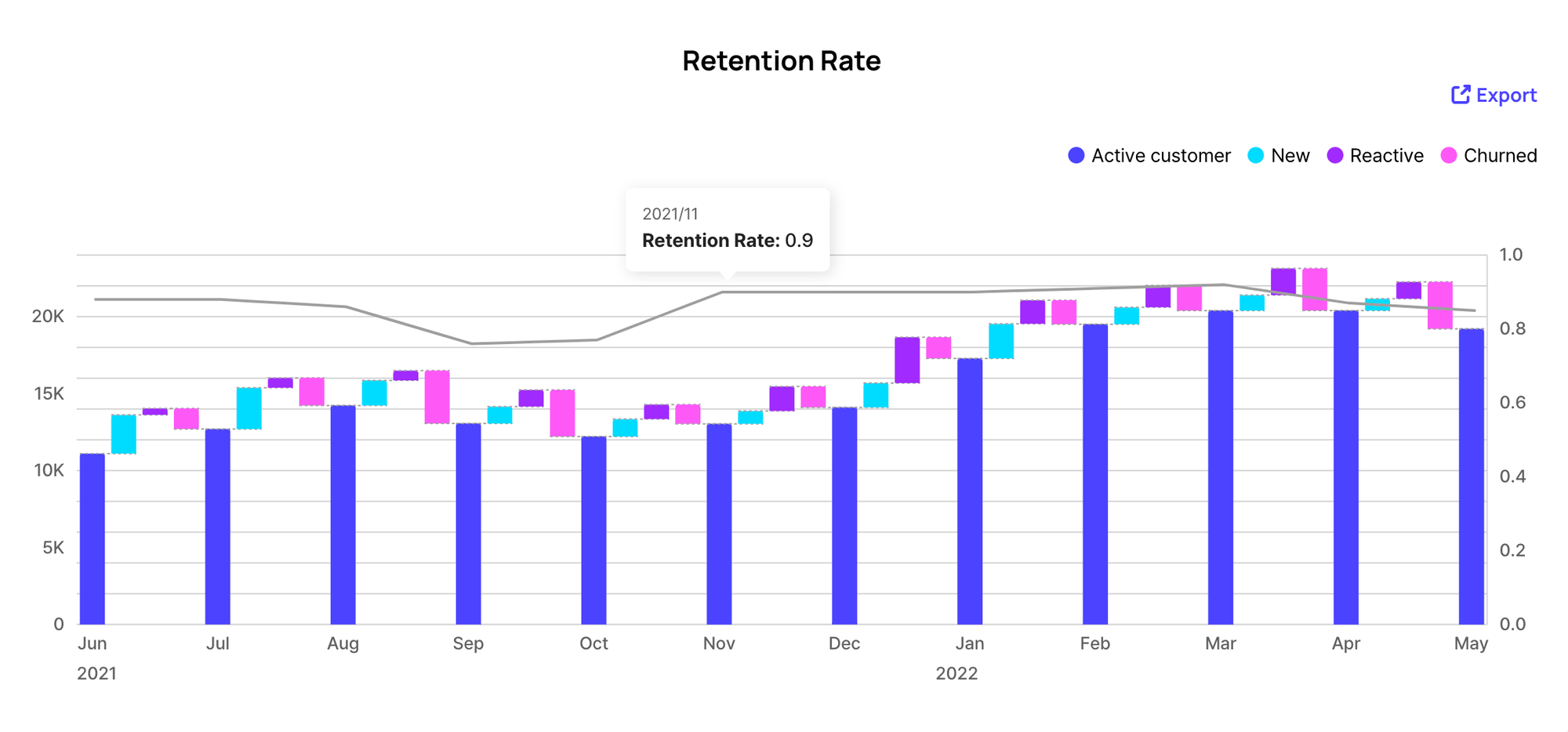
Another important factor to consider is the need to determine the most accurate retention rate. As you can observe in the monthly and quarterly retention charts above, the retention rate for the quarterly period is higher than that for the monthly period. This is quite natural because a customer who consistently makes a purchase from your brand every quarter is included in the numerator for the quarterly retention rate but not in the monthly rate. That being said, when calculating the annual retention rate, you will likely obtain a much higher figure compared to quarterly or monthly rates. Thus, it’s important to analyze your customers' behavior and define the most accurate time window for the retention rate.
3-2. Cohort Chart
The cohort chart is a visual representation of data that allows you to track and analyze the behavior and performance of specific groups or cohorts over time. Cohorts are typically defined by a shared characteristic or experience within a specific time frame, and they are often segmented based on time windows such as weekly, monthly, or quarterly to track customer behavior over a certain period since their acquisition.
a) Customer Lifetime Value
The most popular indicator with the cohort chart could be customer lifetime value. Lifetime value is the value of income a business can obtain through its relationship with customers. It's a concept that explains how much value each customer returns to your business so that you can analyze how much would be appropriate to invest in acquiring new customers or retaining existing ones.
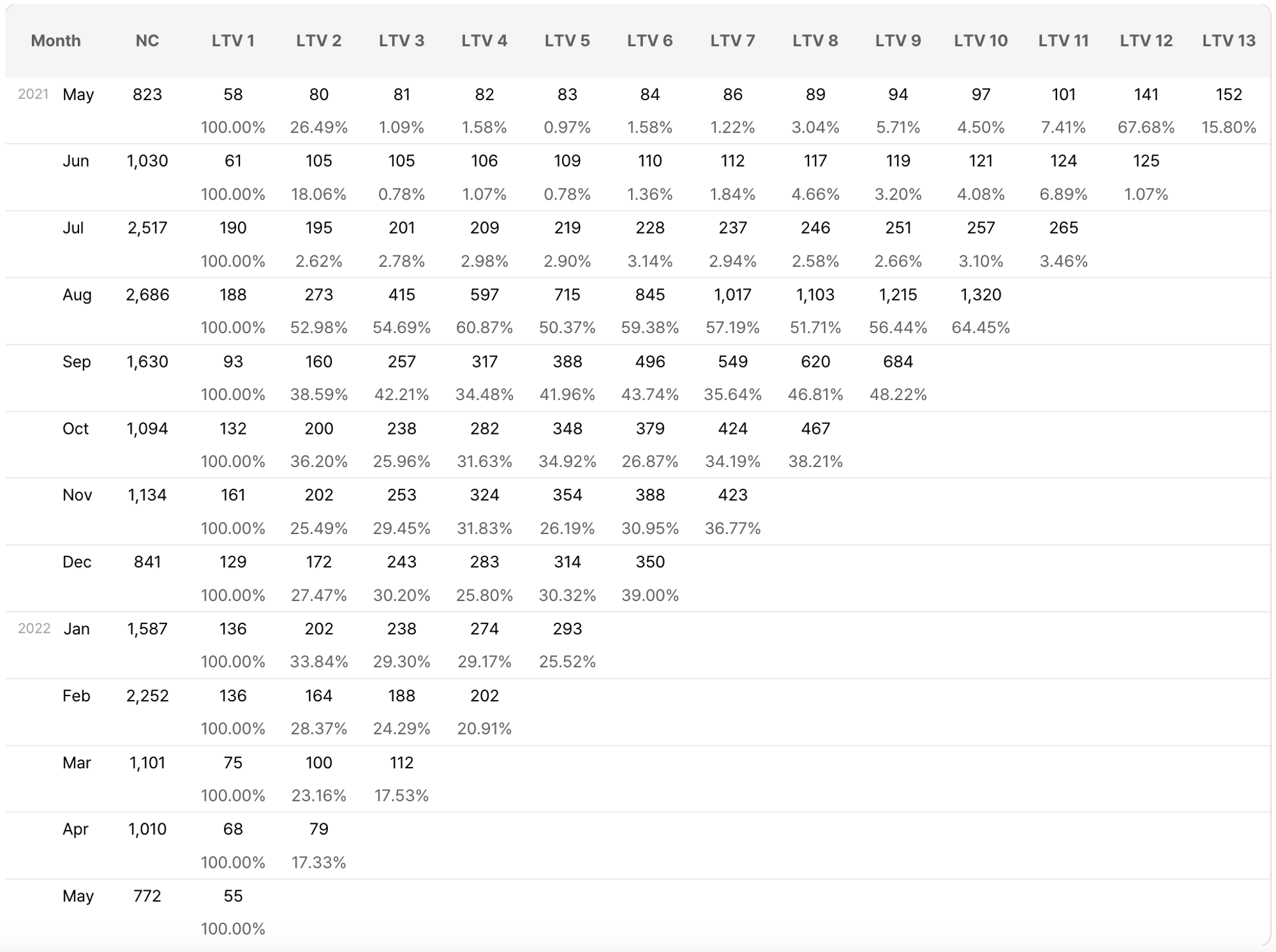
The example is a cohort chart with monthly cohorts for monthly customer lifetime value. The formula is
Total Lifetime Revenue of Cohort Members Since Acquired / Number of Cohort Members
LTV3 means the monetary value that customers in that cohort have spent during the first 3 months since being acquired.
b) Cohort Retention Rate
Another indicator through the cohort chart is the cohort retention rate, which is different from the retention rate explained above. In cohort retention rate, you can measure how many customers retained since their acquisition within a certain timeframe. For instance, if you can see the cohort chart example above, the cohort retention rate is provided right below LTV. You can see the third-month retention rate of the customers who were acquired in August and September is almost doubled over the others. This may be a good point to start analyzing.
3-3. Churn Rate
The churn rate is a critical business metric used to measure the rate at which customers or subscribers discontinue using a product, service, or platform within a specific time period. It holds even greater importance for customer-centric businesses because it directly impacts revenue and growth. Like the retention rate, the churn rate is easy to calculate.
Churn Rate = This Month Churned Customers / This Month Active Customers
However, calculating the churn rate, similar to the retention rate, can be complex, as it depends on the timeframe within which you define a customer as having churned. Churn doesn't necessarily imply that a customer has completely left your business; instead, it signifies a state where the customer is expected to return but has not done so yet. Consequently, churned customers may potentially return later, and we refer to them as reactive customers.
This article is about why retention is important, how to manage it, and which indicators are important for retention. Retentics has a wealth of experience in helping a variety of e-commerce businesses boost healthy growth based on customer retention.
If you are having trouble with customer retention, don’t hesitate to contact Retentics directly!
Written by. Zack Lim
Share article